While breast US has certain advantages over digital mammography it suffers from image artifacts such as posterior acoustic shadowing PAS presence of which often obfuscates lesion margins. However knowledge of the shadowing vascularity and the ability to correlate the mass with the nipple on physical examination will help prevent newcomers from making this mistake.
Basic Principles Radiology Key
Shadowing may result because of reflection of most of the energy by a large impedance discontinuity.
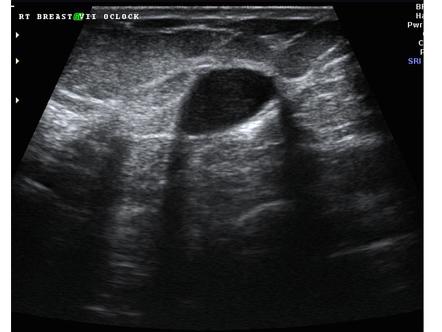
. 70 F remote history of breast cancer and prior lumpectomy. It may be visualized in cases of invasive carcinoma postoperative scar complex sclerosing lesion and fibrous or dense breast tissue 21 22. This loss is displayed in the image as shadowing and is an important sonographic sign for the detection and diagnosis of breast disease.
It is a form of imaging artifact. Upon a screening mammogram and ultrasound they found a 16 oval mass on my right breast. A Breast sonogram reveals focus of intense acoustic attenuation without mass lesion.
As ultrasonic beams propagate through tissues there is a loss of energy by absorption reflection and scattering. Newcomers to breast ultrasound may mistake the nipple for a breast mass because of its hypoechoic appearance shadowing and the intense vascularity beneath it. Although posterior acoustic shadowing is a sonographic feature that is most commonly associated with mammary malignancies this sonographic finding may also be seen with benign breast lesions.
The phenomenon ofacoustic shadowing sometimes somewhat tautologically called posterior acoustic shadowing on an ultrasound image is characterized by a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves. Breast ultrasound US in conjunction with digital mammography has come to be regarded as the gold standard for breast cancer diagnosis. Quantitative Assessment of in vivo Breast Masses using Ultrasound Attenuation and Backscatter Kibo Nam James A.
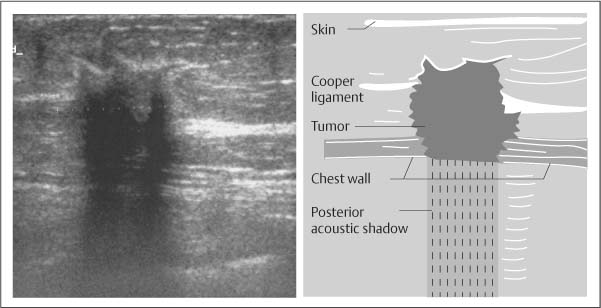
Posterior acoustic enhancement is an indeterminate US finding that can be associated with a variety of entities including normal. Hall Department of Medical Physics University of Wisconsin 1111 Highland Ave Madison WI 53705 Abstract Clinical analysis of breast ultrasound imaging is done qualitatively facilitated with the. Acoustic shadowing from Coopers suspensory ligament mimics breast neoplasm at sonography of nor-mal breast in 43-year-old woman.
You will be shown possible ultrasound correlates on the next slide and be asked to pick the best correlates and. Margin orientation echo pattern and posterior features 1. Acoustic shadowing orig-inates from Coopers ligament be-tween normal fat lobules.
Variable sized fat deposits surrounded by foamy. Which usually do not shadow. On mammography the lesion usually shows localized increased density in the glandular tissue.
Screen detected new mammographic mass Ultrasound is planned as the next step for this finding. Multiple projections from the nodule within or around ducts extending away from the nipple usually seen in larger tumors. If a breast lesion shows posterior acoustic shadowing on ultrasound this means that there is something about the mass or around the mass which attenuates reduces the sonic beam strength in comparison to normal adjacent tissues.
It is a form of imaging artifact. Anyone have benign results with posterior acoustic shadowing. AbstractBreast ultrasound US in conjunction with digital mammography has come to be regarded as the gold standard for breast cancer diagnosis.
Sonographic posterior acoustic shadowing. Zagzebski and Timothy J. Posterior acoustic shadowing is a suspicious finding and may be seen in cases of invasive carcinoma postoperative scar complex sclerosing lesion or macrocalcifications and may even be seen in patients with dense breast tissue.
It is wider than tall with macrolobulations no calcifications and posterior acoustic shadowing. If the lesions combine other features of malignancy such as spiculated margin nonparallel orientation and posterior shadowing Are Irregular Hypoechoic Breast Masses on Ultrasound. Posterior acoustic shadowing may indicate pathologic changes inciting desmoplastic reaction that can attenuate the ultrasound beam and are described in both benign and malignant conditions.
Irregular hypoechoic masses on breast ultrasound are usually considered suspicious lesions. Posterior acoustic shadowing PAS can bias breast tumor segmentation and classification in ultrasound images. Acoustic shadowing originates from Coopers ligament between normal fat lobules.
Posterior acoustic shadowing is suspicious for breast cancer If a breast lesion shows posterior acoustic shadowing on ultrasound this means that there is something about the mass or around the mass which attenuates reduces the sonic beam strength in comparison to normal adjacent tissues. The phenomenon of acoustic shadowing sometimes somewhat tautologically called posterior acoustic shadowing on an ultrasound image is characterized by a signal void behind structures that strongly absorb or reflect ultrasonic waves. Breast sonogram reveals focus of intense acoustic attenuation without mass lesion.
B Sonogram obtained after mild addi-. Posterior acoustic shadowing Non-circumscribed margins Non-palpable Controversial and age dependent Not new Case 3. Developing asymmetry upper inner breast mid depth.
DMP usually shows nonspecific parenchymal enhancement rather than an irregular enhancing mass on MRI. Although posterior acoustic shadowing is a sonographic feature that is more commonly associated with breast malignancies this sonographic. It is the posterior acoustic shadowing that is freaking me out.
In this paper half-contour features are proposed to classify benign and malignant breast tumors with PAS considering the fact that the upper half of the tumor contour is less affected by PAS. While breast US has certain advantages over digital mammography it suffers from image artifacts such as posterior acoustic shadowing PAS presence of which often obfuscates lesion margins. Hypoechoic irregular mass with posterior shadowing indistinct margins and vascular flow measuring 11 x 4 x 9 mm.
An irregular hypoechoic mass with intense posterior acoustic shadowing can be typically seen on US and can mimic breast malignancy Fig. Acoustic shadowing from Coopers suspensory ligament mimics breast neoplasm at sonography of normal breast in 43-year-old woman.

The Relationship Between Lateral Acoustic Shadow Feature On Ultrasound Download Scientific Diagram

Ultrasound Image Of A Breast Cancer With Irregular Borders Angular Download Scientific Diagram
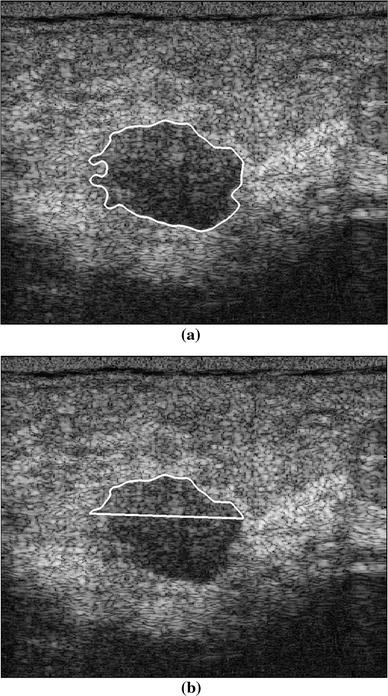
Classification Of Benign And Malignant Breast Tumors In Ultrasound Images With Posterior Acoustic Shadowing Using Half Contour Features Springerlink

Sonographic Evaluation Of Benign And Malignant Breast Masses Iame

Benign And Malignant Characteristics Of Breast Lesions At Ultrasound Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org

Posterior Acoustic Shadowing In Benign Breast Lesions Weinstein 2004 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Posterior Acoustic Shadowing In Benign Breast Lesions Weinstein 2004 Journal Of Ultrasound In Medicine Wiley Online Library

Transverse Ultrasound Of The Left Breast Demonstrates An Irregular Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments
Post a Comment